≡ Sunburn
The best way to care for Sunburned Skin
Φ 曬傷
What is Sunburn?
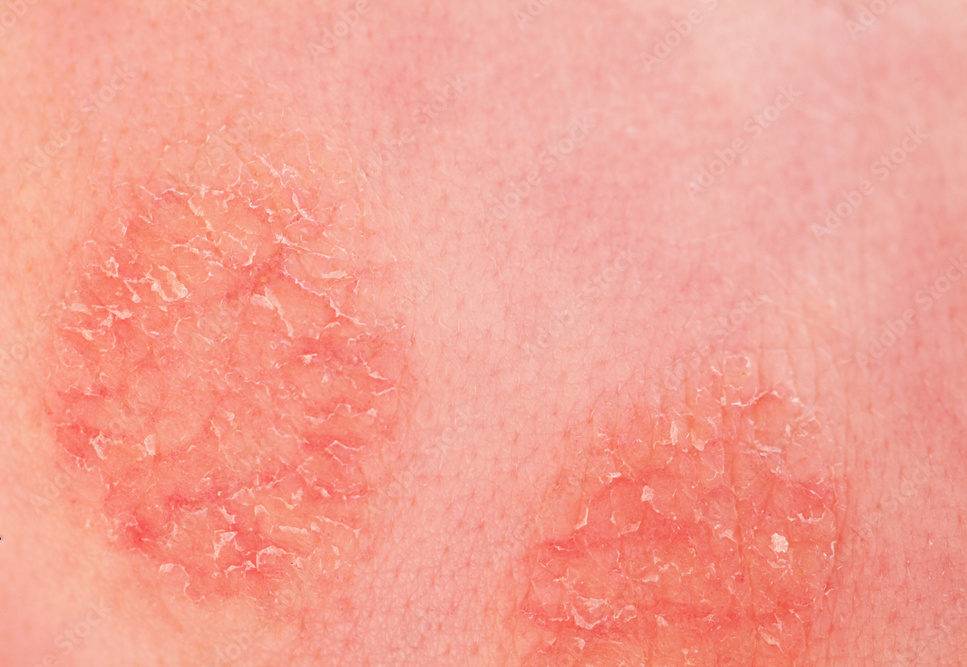
Sunburn is red, painful skin that feels hot to the touch. It usually appears within a few hours after too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from sunshine or artificial sources, such as sunlamps. Home remedies can usually provide sunburn relief, but sunburn may take days to fade.
Intense, repeated UV light exposure that results in sunburn increases the risk of other skin damage, such as dark spots, rough spots, and dry or wrinkled skin. It also raises the risk of skin cancers such as melanoma.
You can prevent sunburn and related conditions by protecting your skin. This is especially important when you’re outdoors, even on cool or cloudy days.
What are the symptoms of Sunburn?
Sunburn signs and symptoms can include:
- Changes in skin tone, such as pinkness or redness
- Skin that feels warm or hot to the touch
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling
- Small fluid-filled blisters, which may break
- Headache, fever, nausea and fatigue, if the sunburn is severe
- Eyes that feel painful or gritty
- Any exposed part of your body — including your earlobes, scalp and lips — can burn. Even covered areas can burn if, for example, your clothing has a loose weave that allows ultraviolet (UV) light through. Your eyes, which are extremely sensitive to the sun’s UV light, also can burn.
Sunburn signs and symptoms usually appear within a few hours after sun exposure. But it may take a day or more to know how severe the sunburn is.
Within a few days, your body may start to heal itself by peeling the damaged skin’s top layer. After peeling, your skin may temporarily have an irregular color and pattern. A bad sunburn may take several days to heal.
Risk factors for sunburn include:
- Having light skin, blue eyes, and red or blond hair
- Living or vacationing somewhere sunny, warm or at high altitude
- Working outdoors
- Swimming or spraying your skin with water, as wet skin tends to burn more than does dry skin
- Mixing outdoor recreation and drinking alcohol
- Regularly exposing unprotected skin to UV light from sunlight or artificial sources, such as tanning beds
- Taking a drug that makes you more likely to burn (photosensitizing medications)
Who gets Sunburns?
Factors More Prone to Sunburn: fair skin, blue eyes, and red or blond hair.
Living or vacationing somewhere sunny, warm or at high altitude, working outdoors, swimming or spraying your skin with water, as wet skin tends to burn more than does dry skin.
Mixing outdoor recreation and drinking alcohol.
Regularly exposing unprotected skin to UV light from sunlight or artificial sources, such as tanning beds.
Taking a drug that makes you more likely to burn (photosensitizing medications).
What Causes Sunburn and risk factors of Sunburn?
Sunburn is caused by too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. UV light may be from sunlight or artificial sources, such as sunlamps and tanning beds.
Melanin is the dark pigment in the skin’s outer layer that gives skin its normal color. When you’re exposed to UV light, your body protects itself by producing melanin faster. The extra melanin creates tan. A suntan is the body’s way of blocking UV rays to prevent sunburn. But the protection only goes so far. Too much UV light causes skin to burn.
You can get sunburn on cool or cloudy days. Snow, sand, water and other surfaces can reflect UV rays that cause the skin to burn too.
Recommended Treatment for Sunburn
- Hydrafill Facial – Needleless Mesotherapy
- Soothing Facial – Needleless Mesotherapy
- One Love Facial with Hydrating Eye & Lip Mask
- Oceanic Facial
Recommended Resource/Product for Sunburn
- Clayton Shagal Clinical Elasthy Extract
- Clayton Shagal Clinical Colhy Extract
- Clayton Shagal Hyaluronic Acid Serum
- Clayton Shagal Sensi Derm Cream
- Clayton Shagal Illumine Cream
- Clayton Shagal Hydra One Cream
- Clayton Shagal Cucumber and Avocado Mask
- Clayton Shagal Elastin Serum
- Clayton Shagal Gel Lotion Cleanser
- Clayton Shagal Milk Cleanser
- Clayton Shagal Body Cream
- Clayton Shagal Collagen Serum
- TIZO2® FACIAL PRIMER SUNSCREEN Non-Tinted Matte Finish SPF 40
- TIZO ULTRA ZINC BODY & FACE SUNSCREEN non-tinted dewy finish SPF 40
- Engel Gesicht Hyaluronic Acid Collagen Sheet Face Mask
- Nano White Effect Brightening Gel Masque
- Clayton Shagal Hydra Derm Cream
- Clayton Shagal Clinical Colhy Gel
- Clayton Shagal Clinical Elasthy Gel
- Clayton Shagal Collagen Gel Plus
- Clayton Shagal Elastin Gel Plus
- Clayton Shagal Collagen Gel
- Clayton Shagal Elastin Gel
On What Matters
Conditions & Care

A Colourful Mind & Heart
Whatever is true, whatever is noble, whatever is right, whatever is pure, whatever is lovely, whatever is admirable—if anything is

The Selfology Skincare Guide—AUTUMN EDITION—A Comprehensive Skincare Guide for All Skin Types and Complexions
selfology.co/skincare